BIT.SHES TOOLBOX
Art + Blockchain + Inclusion
Learning Center: Blockchain Basics

What is Blockchain?
Who Invented Blockchain?
Types of Blockchains
1. Public Blockchain
Public blockchains are ledger systems that are decentralized, which means that no one single entity has control over the network. They are open to the public and accessible by all. There are no restrictions on the participants, and anyone can view current and old records or transactions and verify or validate them. This accessibility does not mean that transactions can be tampered with; rather, it means added security exists through public transparency. Public blockchains are very secure because this transparency protects records from being changed by an external body.
2. Private Blockchain
3. Consortium Blockchain
Consortium blockchains are like private blockchains, but rather than being managed by a single entity, a group of organizations governs them. They combine private and public blockchains, and as such, some parts of the blockchain are made public while others are kept private. As a result, consortium blockchains allow for more efficiency both individually and as a group. These blockchains are often used by banks, government institutions, and other related organizations.
4. Hybrid Blockchain
Hybrid blockchains combine private both public blockchains and have characteristics of each. A hybrid blockchain combines the privacy of a private blockchain with the transparency and security of a public blockchain. The users control access to data that doesn’t require permission, while other data is only available on a private network to those given access.
How is Blockchain Used?
Blockchain is seen by many as a revolutionary technology that challenges the conventional methods of doing business and making transactions for both individuals and organizations. Let’s look at some real-life applications of blockchain technology:
● Blockchain and Finance
● Smart Contracts
● Blockchain and Art
● Blockchain and Music
● Blockchain and Philanthropy
Key Takeaways:
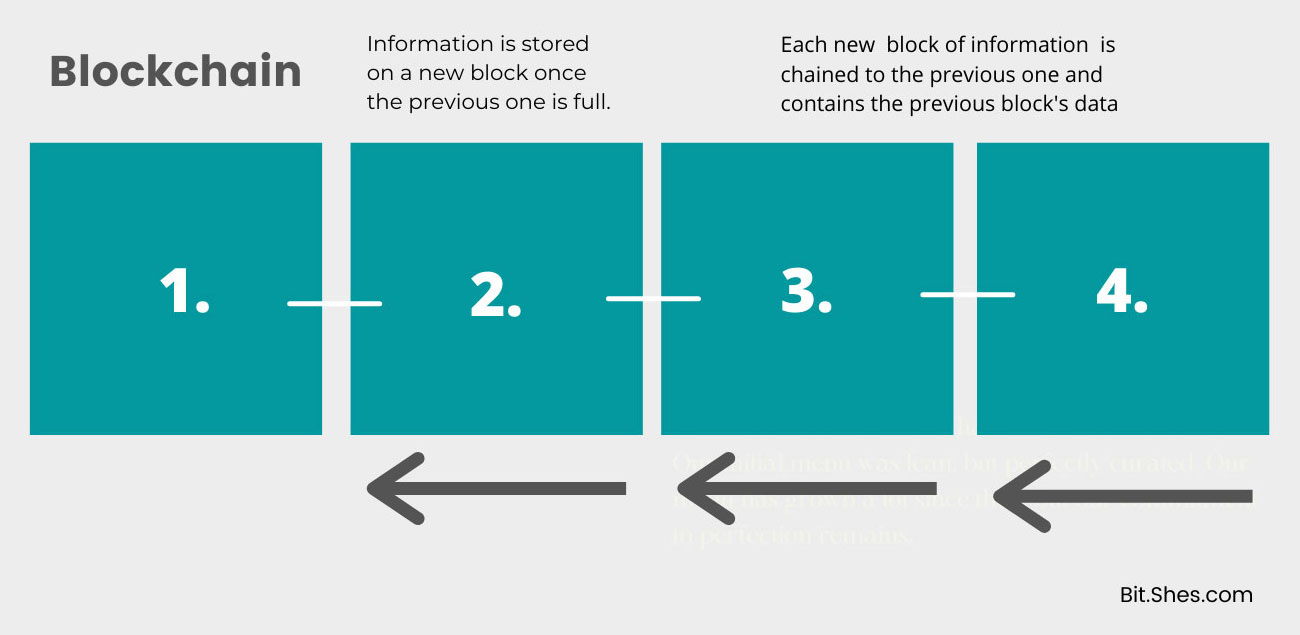
- A blockchain is a digital ledger that stores transactions and records information in blocks.
- A blockchain stores information on its network in a way that is immutable, tamper-proof, and decentralized.
- The first blockchain was released by Bitcoin creator Satoshi Nakamoto, the true identity of whom remains unknown.
- There are currently four main types of blockchains; public, private, consortium, and hybrid.
- Blockchain technology is spread across many industries and its use cases are rapidly expanding